| [1] 裴国献,张元智,主编.数字骨科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009:502-503.
[2] 王洪伟,王晓红.有限元分析法在脊柱骨折研究中的应用进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(6):1074-1076.
[3] 赵凡,刘正,王炳强,等.有限元模拟单节段腰椎小关节分级切除对腰椎稳定性的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2015,95(13): 973-977.
[4] 黄振宇,董跃福.基于有限元方法的正常和早期OA膝关节生物力学行为比较[J].中国数字医学,2015,(5):6-9.
[5] 中国解剖学会体质调查委员会编.中国人解剖数值[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2002:27.
[6] Moyer RF, Ratneswaran A, Beier F, et al.Osteoarthritis year in review 2014: mechanics--basic and clinical studies in osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014; 22(12):1989-2002.
[7] Donahue TL, Fisher MB, Maher SA. Meniscus mechanics and mechanobiology.J Biomech. 2015; 48(8):1341-1342.
[8] Duchman KR, DeVries NA, McCarthy MA, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction.Iowa Orthop J. 2013; 33:64-69.
[9] Hopper GP, Leach WJ, Rooney BP, et al. Does degree of trochlear dysplasia and position of femoral tunnel influence outcome after medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction? Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42(3):716-722.
[10] DeVries Watson NA, Duchman KR, et al. A Finite Element Analysis of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction.Iowa Orthop J. 2015; 35:13-19.
[11] Stephen JM, Kittl C, Williams A, et al. Effect of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Method on Patellofemoral Contact Pressures and Kinematics.Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(5):1186-1194.
[12] Filardi V. Stress shielding in the bony chain of leg in presence of varus or valgus knee.J Orthop. 2015; 12(2): 102-110.
[13] Mologne TS, Cory E, Hansen BC, et al. Osteochondral allograft transplant to the medial femoral condyle using a medial or lateral femoral condyle allograft: is there a difference in graft sources? Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42(9):2205-2213.
[14] Laprade RF, Wijdicks CA.Surgical technique: development of an anatomic medial knee reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(3): 806-814.
[15] Steinbrück A, Woiczinski M, Weber P, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty: a numerical study with a dynamic force controlled knee model.Biomed Eng Online. 2014; 13:91.
[16] Barrow AE, Pilia M, Guda T, et al. Femoral suspension devices for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: do adjustable loops lengthen? Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42(2):343-349.
[17] Deo S, Getgood A. A Technique of Superficial Medial Collateral Ligament Reconstruction Using an Adjustable-Loop Suspensory Fixation Device.Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(3):e261-265.
[18] Born TR, Biercevicz AM, Koruprolu SC, et al. Biomechanical and Computed Tomography Analysis of Adjustable Femoral Cortical Fixation Devices for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in a Cadaveric Human Knee Model.Arthroscopy. 2016; 32(2):253-261.
[19] Toutoungi DE,Lu Tw,Leardini A,et al.Cruciate ligament forces in the knee during rehabilitation exercise.Clin Biomech. 2000;15(3):176-187.
[20] Zheng N,Fleisig GS,Escamilla RF,et a1.An analytical model of the knee for estimation of internal forces duringexercise.J Biomech. 1998;31:963-967.
[21] Huss RA,Holstein H,O,Connor JJ. A mathematical model of forces in the knee under isometric quadriceps contractions. Clin Biomech. 2000;15:112-122.
[22] Wongchaisuwat C, Hemami H,Bucher HJ.Control of sliding and rolling at natural joints. J Biomech Eng. 1984;106(4):368-375.
[23] Engin AE,Turner ST. An innovative approach to the solution of highly nonlinear dynamics problems associated with joint biomechanics.Proceedings of the 1991 Biomechanics Symposium,Ohio State University, Columbus,OH,1991:225.
[24] Engin AE,Turner ST.Improved dynamics model of the human knee joint and its response to impact loading on the lower leg. J Biomech Eng,1993;115(2):137-143.
[25] Catalfamo PF, Aguiar G, Curi J, Braidot A. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: Compensation during Gait using Hamstring Muscle Activity.Open Biomed Eng J. 2010; 4:99-106.
[26] Kazemi M, Dabiri Y, Li LP. Recent advances in computational mechanics of the human knee joint.Comput Math Methods Med. 2013; 2013:718423.
[27] Erdemir A. Open Knee: A Pathway to Community Driven Modeling and Simulation in Joint Biomechanics.J Med Device. 2013; 7(4):0409101-409101.
[28] Opar DA, Williams MD, Timmins RG, et al. Knee flexor strength and bicep femoris electromyographical activity is lower in previously strained hamstrings.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2013; 23(3):696-703.
[29] Opar DA, Serpell BG. Is there a potential relationship between prior hamstring strain injury and increased risk for future anterior cruciate ligament injury?Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 95(2):401-405.
[30] Meng Q, Jin Z, Wilcox R, et al. Computational investigation of the time-dependent contact behaviour of the human tibiofemoral joint under body weight.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014; 228(11):1193-1207.
[31] González-Carbonell RA, Ortiz-Prado A, Jacobo-Armendáriz VH, et al. 3 D patient-specific model of the tibia from CT for orthopedic use.J Orthop. 2015; 12(1):11-16.
[32] Baldwin MA, Clary CW, Fitzpatrick CK, et al. Dynamic finite element knee simulation for evaluation of knee replacement mechanics.J Biomech. 2012;45(3): 474-483.
[33] Fitzpatrick CK, Komistek RD, Rullkoetter PJ. Developing simulations to reproduce in vivo fluoroscopy kinematics in total knee replacement patients.J Biomech. 2014; 47(10):2398-2405.
[34] Fitzpatrick CK, Rullkoetter PJ. Estimating total knee replacement joint load ratios from kinematics.J Biomech. 2014; 47(12):3003-3011.
[35] Pianigiani S, Vander Sloten J, Pascale W, et al. A new graphical method to display data sets representing biomechanical knee behaviour. J Exp Orthop. 2015; 2(1):18.
[36] Nenezic D, Kocijancic I .The value of the sagittal-oblique MRI technique for injuries of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee.Radiol Oncol. 2013; 47(1):19-25.
[37] Muhle C, Ahn JM, Dieke C. Diagnosis of ACL and meniscal injuries: MR imaging of knee flexion versus extension compared to arthroscopy. Springerplus. 2013; 2(1):213.
[38] Kosaka M, Nakase J, Toratani T, et al. Oblique coronal and oblique sagittal MRI for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears and evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament remnant tissue.Knee. 2014; 21(1): 54-57.
[39] Taketomi S, Inui H, Sanada T, et al. Remnant-preserving anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using a three-dimensional fluoroscopic navigation system.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2014;26(3): 168-176.
[40] Araki D, Kuroda R, Matsumoto T, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of bone tunnel changes after anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using multidetector-row computed tomography.Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42(9): 2234-2241. |
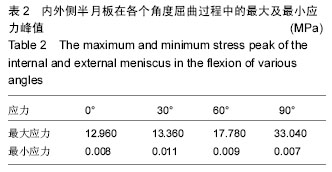
.jpg)
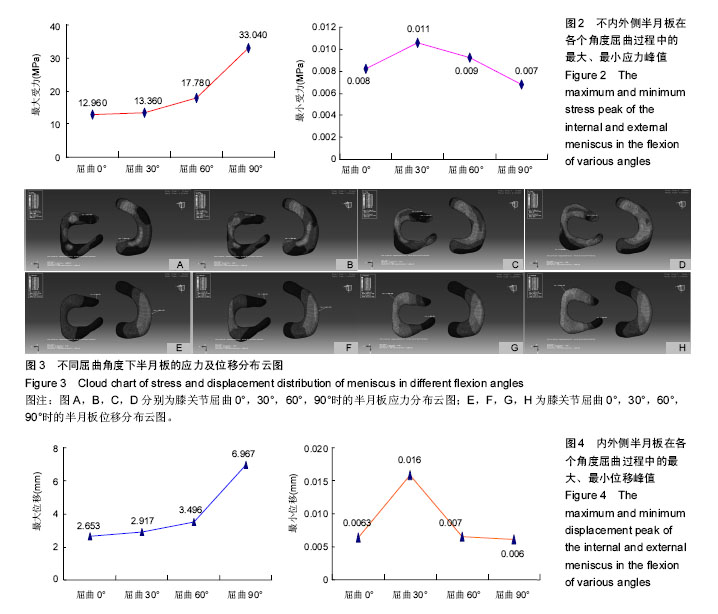
.jpg)
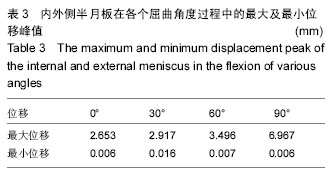
.jpg)
.jpg)